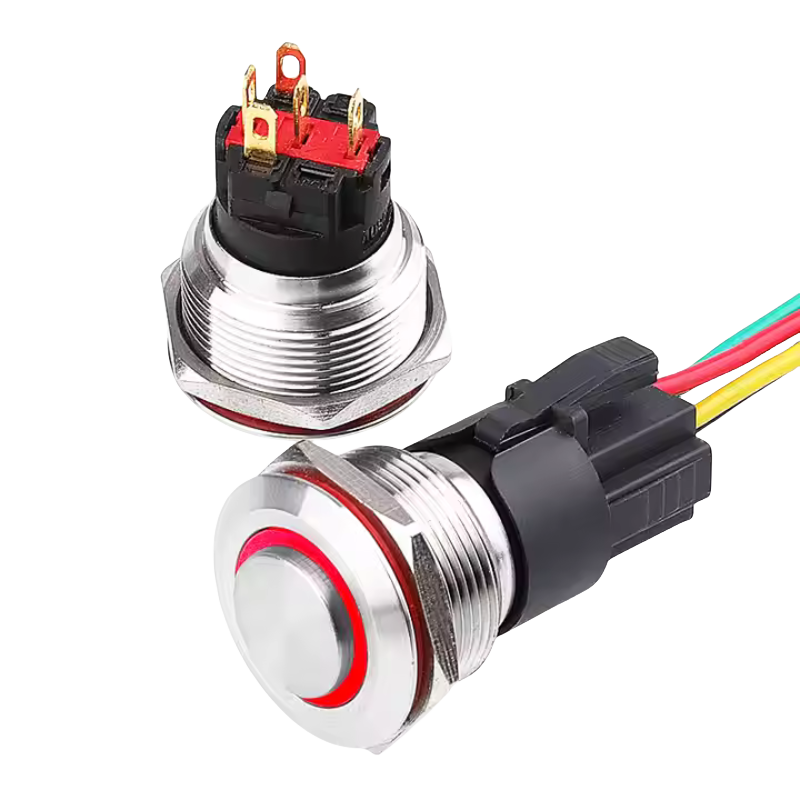
More Than Just a Button
In an age where touchscreens, voice commands, and gesture-based interfaces dominate our interaction with technology, it might seem like the humble push button has been left behind. But in reality, one of the most enduring components in modern electronics is still widely used across industries — the metal push button switch.
Despite its simple appearance, this component plays a crucial role in everything from factory automation to smart home systems. It’s not just about turning something on or off; it’s about reliability, precision, and human connection with machines.
In this article, we’ll explore why metal push button switches remain relevant, how they’re built, and why their design continues to evolve alongside modern technology.
A Brief History: From Mechanical Levers to Precision Components
The concept of manually activating a device through physical pressure dates back centuries. Early forms of mechanical switches were found in telegraphs, elevators, and industrial machines. However, the modern push button as we know it began taking shape during the 20th century, especially with the rise of electrical engineering.
Initially made from brass or steel, early push buttons were primarily used in control panels and heavy machinery due to their durability. Over time, as materials science advanced, manufacturers began using stainless steel, aluminum, and other corrosion-resistant metals to improve longevity and aesthetics.
Today’s metal push button switches are far more than simple on/off toggles. They incorporate features such as LED lighting, waterproofing, and even smart connectivity, making them indispensable in both traditional and cutting-edge applications.
What Makes a Metal Push Button Switch?
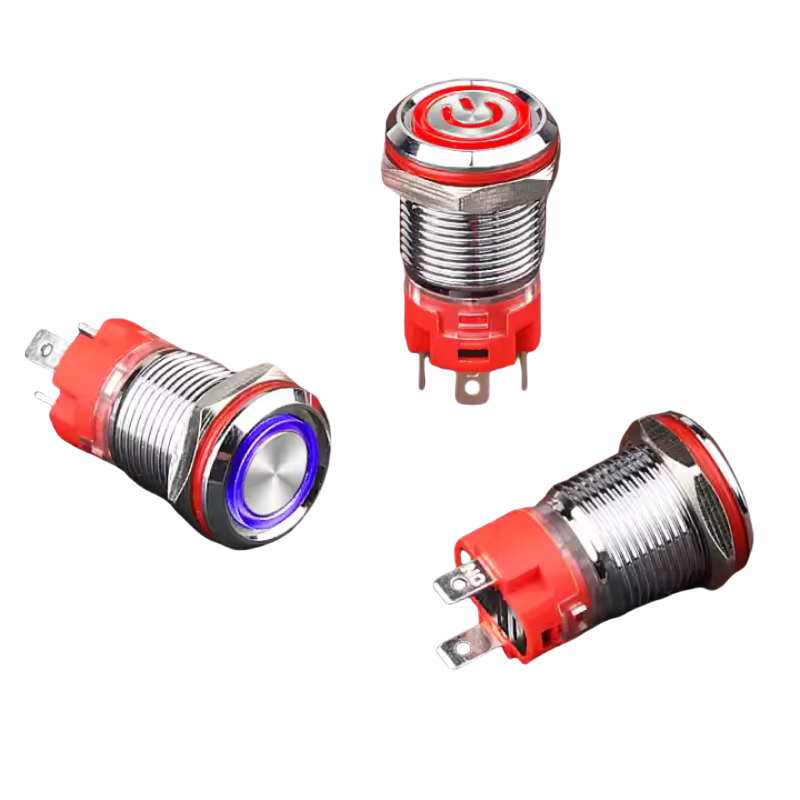
At its core, a metal push button switch is a manually operated electrical component that opens or closes a circuit when pressed. It typically consists of:
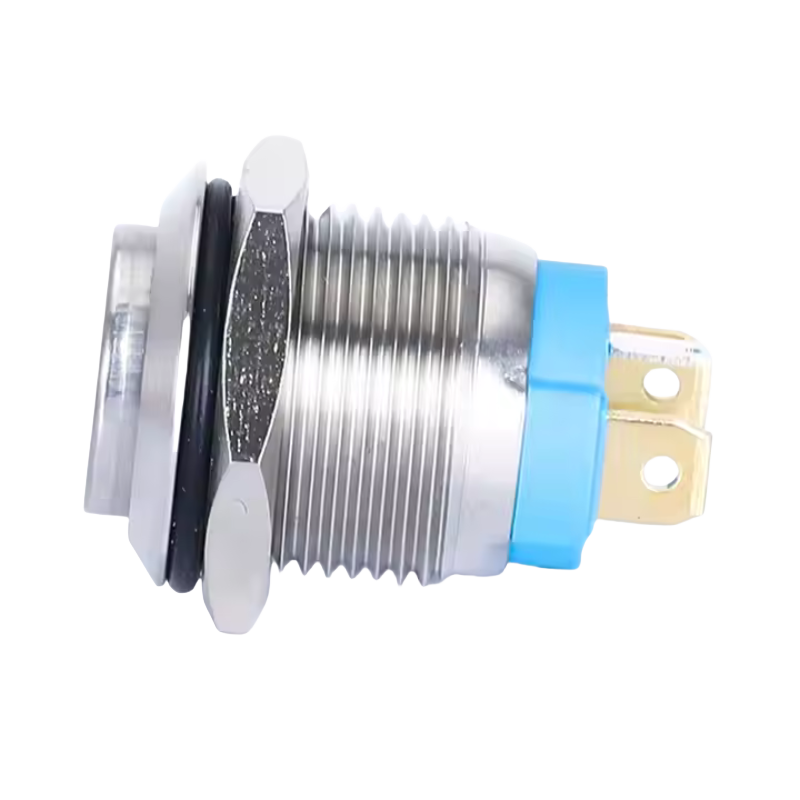
- Metal Actuator: Usually made from stainless steel, aluminum, or brass.
- Contact Terminals: These connect the switch to the rest of the electrical system.
- Spring Mechanism: Returns the button to its original position after being pressed.
- Optional Features: LED illumination, waterproof seals, self-locking functions, and custom labeling.
These switches come in various sizes (commonly 12mm, 16mm, 19mm, 22mm, or 30mm) and configurations (such as momentary, latching, SPST, DPDT, etc.), allowing them to be integrated into nearly any application.
Why Choose Metal Over Plastic?
While plastic push buttons may be lighter and cheaper to produce, metal offers several distinct advantages:
1. Durability
Metal push buttons can withstand millions of presses without failure. This makes them ideal for high-use environments such as factory floors, public transport controls, and industrial equipment.
2. Environmental Resistance
Many metal switches are rated for IP65, IP67, or even IP69K, meaning they can resist dust, water, and high-pressure cleaning. This makes them suitable for outdoor use, food processing plants, or medical devices requiring frequent sterilization.
3. Aesthetic Appeal
Unlike plastic, metal offers a premium look and feel. Whether brushed, polished, or coated, metal buttons convey quality and sophistication — which is why you’ll often find them in luxury appliances, automotive interiors, and architectural lighting controls.
4. Tactile Feedback
One of the biggest selling points of a well-made metal push button is its tactile response. Users can feel when the button is activated, providing immediate confirmation without needing visual or auditory cues.
Types of Metal Push Button Switches
Metal push buttons aren’t one-size-fits-all. Here are some common types based on function and design:
Momentary vs. Latching (Self-Locking)
- Momentary Switches: Return to their original state once released. Think of a doorbell or horn — press and release.
- Latching (Self-Locking) Switches: Stay in the pressed position until pressed again. Commonly used for power switches.
Illuminated vs. Non-Illuminated
- Illuminated Buttons: Feature built-in LEDs for visibility in low-light conditions. Available in single-color or RGB options.
- Non-Illuminated Buttons: Used in minimalist designs or where light isn’t necessary.
Contact Configurations
Switches also vary in how they route electrical current:
- SPST (Single Pole Single Throw) – Simple on/off switching.
- SPDT (Single Pole Double Throw) – Can switch between two circuits.
- DPDT (Double Pole Double Throw) – Handles higher currents and multiple circuits simultaneously.
Where Are Metal Push Button Switches Used?
Thanks to their versatility, metal push buttons are used in a wide range of applications:
Industrial & Automation Systems
Factory machines, conveyor belts, emergency stop systems, and control panels rely heavily on durable metal switches. Their ability to withstand harsh environments makes them indispensable in manufacturing.
Automotive Industry
From dashboard controls to steering wheel buttons, metal push buttons offer a refined feel in high-end vehicles. Electric cars, in particular, have embraced sleek metal buttons for gear selectors and climate controls.
Home Appliances
Luxury ovens, refrigerators, and coffee machines often feature metal buttons for a premium user experience. Smart home devices, such as thermostats and lighting controllers, also integrate metal push buttons for tactile interaction.
Medical Equipment
Precision and hygiene are key in healthcare settings. Metal push buttons with sealed designs and antimicrobial finishes are commonly used in MRI machines, patient monitors, and lab instruments.
Public Infrastructure
Elevator call buttons, ticket machines, and vending systems frequently use metal push buttons due to their long lifespan and resistance to vandalism.
How to Choose the Right Metal Push Button Switch
When selecting a metal push button switch, consider the following factors:
Size
Common sizes include 12mm, 16mm, 19mm, 22mm, and 30mm. The size should match the panel cutout and intended use.
Voltage & Current Rating
Ensure the switch can handle the load of your circuit. For example, a 24V / 5A rating is typical for many general-purpose applications.
Waterproof Rating
For outdoor or wet environments, choose a switch with at least IP65 or IP67 protection.
Function Type
Decide whether you need a momentary or latching switch, and what kind of contact configuration (e.g., 1NO1NC, 2NO2NC).
Aesthetics
Color, finish, and illumination style can significantly impact the overall design of your product.
Trends and Innovations in Metal Push Button Switch Design
As technology advances, so too do the features and capabilities of metal push button switches:
Customizable Lighting
Modern switches now support RGB LEDs, allowing users to change colors via apps or voice assistants. Some even sync with ambient lighting systems for mood-based interfaces.
Smart Integration
Some models are designed to work with IoT platforms, sending real-time data about usage patterns or maintenance needs.
Eco-Friendly Materials
With sustainability becoming a priority, manufacturers are exploring recyclable metals and energy-efficient LED lighting.
Haptic Feedback
Newer switches incorporate vibration or sound feedback to enhance the user experience, especially in silent environments.
Small Component, Big Impact
While the metal push button switch may seem like a minor part of the technological puzzle, its influence is widespread and enduring. From heavy industry to everyday household devices, it serves as a bridge between human intention and machine action.
Its combination of durability, functionality, and aesthetic appeal ensures that it remains a vital component in both traditional and cutting-edge applications. As design trends continue to favor minimalism and tactile interaction, the future looks bright for the humble metal push button switch.
So next time you press a button to start your car, turn on a light, or call an elevator — take a moment to appreciate the craftsmanship and engineering behind that satisfying click.